English may not have as many verb forms as other languages you know—but those few forms come with a lot of complications!
The simple past is no different: There is a lot to learn, from irregular verbs to forming questions and negative sentences. Plus you have to understand the difference between the simple past and other tenses.
Here’s everything you need to know about how to form the simple past in English, how it’s pronounced, and when to use it!
In this post:
When is the simple past used?
How do you form the simple past?
Verbs with irregular simple past forms
Negation of simple past
Questions in the simple past
Pronunciation of the simple past
Simple past vs. simple present perfect
When is the simple past used?
In English, the simple past is used to talk about things that started and ended in the past. For example:
I called my mom last night.
We played basketball yesterday.
They went to the store two days ago.
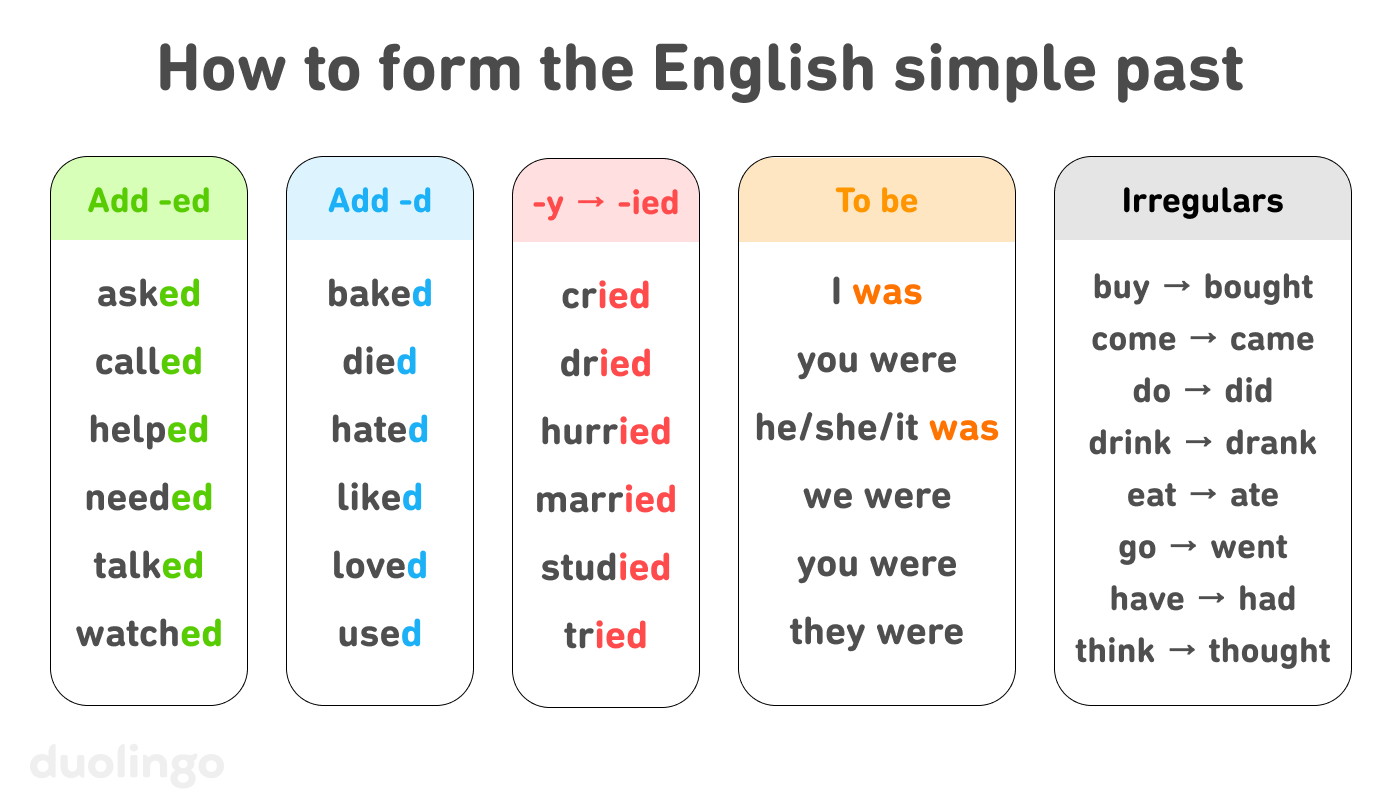
How do you form the simple past?
Most commonly, the simple past follows a simple formula:
For example:
| BASE VERB | SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| talk | talked | Amy talked to her girlfriend on the phone yesterday. |
| watch | watched | Last month, they watched a lot of scary movies. |
| ask | asked | I asked two questions. |
However, if the base form of a regular verb already ends with an ‑e, you only need to add a ‑d for the past:
| BASE VERB | SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| use | used | We used your pen. |
| die | died | Lucy’s cat died yesterday. |
| bake | baked | Vikram baked a big cake. |
If the base form of a regular verb ends with a consonant followed by a ‑y, change the ‑y to ‑i and then add ‑ed:
| BASE VERB | SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| try | tried | I tried the soup. |
| marry | married | She married my brother. |
| hurry | hurried | They hurried to the car. |
Finally, if the base form of a regular verb ends with consonant-vowel-consonant, you usually double the last consonant and then add ‑ed:
| BASE VERB | SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| plan | planned | We planned the party. |
| stop | stopped | Junior stopped the movie. |
| wag | wagged | The dog wagged its tail. |
Past forms of irregular verbs
One of the tricky parts of the simple past is that there are many irregular verbs, for which the past form of the verb does not follow the regular ‑ed pattern. Some common irregular verbs and their past tense forms include:
| BASE VERB | SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| bring | brought | Zari and Lily brought the cake. |
| buy | bought | Lucy bought a new coat. |
| can | could | She could walk fast. |
| come | came | They came to the house. |
| do | did | I did my homework. |
| drink | drank | Junior drank the milk. |
| eat | ate | We ate at the restaurant. |
| find | found | They found their car. |
| go | went | It went in that box. |
| have | had | The dress had two buttons. |
| think | thought | Eddy thought he was lost. |
In addition to the irregular verbs above, the verb to be is also irregular. I and he/she/it take the past form was, while you, we, you (plural) and they all take the past form were:
| SIMPLE PAST | EXAMPLE | |
|---|---|---|
| I | was | I was thirsty last night. |
| you (singular) | were | You were at school last week. |
| he/she/it | was | It was so hot yesterday! |
| we | were | We were much younger back then. |
| you (plural) | were | You were all so great in that play last year. |
| they | were | They were at Grandma’s house two days ago. |
Negation of simple past
To form negative sentences in the simple past, add the words did not before the base form of the verb. Did not is also often written as the contraction didn’t:
| AFFIRMATIVE | NEGATIVE | NEGATIVE WITH CONTRACTION |
|---|---|---|
| I watched the movie. | I did not watch the movie. | I didn’t watch the movie. |
| They played in the house. | They did not play in the house. | They didn’t play in the house. |
| He bought new shoes. | He did not buy new shoes. | He didn’t buy new shoes. |
Questions in the simple past
You can ask questions using the simple past. Usually with questions in this tense, you add the word did. However, you don’t need to add did for questions using was or were. Here are the most common types of questions and resources to study them more:
Yes/no questions
Q: Did you close the door?
A: Yes, I closed the door.
Q: Was Zari excited?
A: Yes, Zari was definitely excited.
Wh- questions
Q: Where did they watch the movie?
A: They watched the movie at home.
Q: When was Oscar in Italy?
A: He was in Italy last year for an art symposium.
Tag questions
You didn’t buy more cheese, did you?
She didn’t lose her keys, did she?
Pronunciation of the simple past
The ‑ed at the end of regular verbs in the simple past is pronounced differently depending on the last sound in the base verb. (Remember to think about the last sound and not the last letter!)
If the base form of the verb ends with a voiceless sound (this means you don’t vibrate your vocal folds), the ‑ed is pronounced as “t.” Voiceless sounds include “p,” “f,” “s,” “sh,” “ch,” and “k.” For example, the ‑ed at the end of pushed, watched, and kissed are all pronounced “t.”
If the base form of the verb ends with a voiced sound (this means you vibrate your vocal folds), the ‑ed is pronounced as “d.” Voiced sounds include all vowel sounds as well as “b,” “m,” “w,” “v,” “th" (as in the), “z,” “r,” “y” (as in you), “n,” and “g." For example, the ‑ed at the end of played, loved, and rained are all pronounced “d.”
Finally, if the base form of the verb ends with the sound “d” or “t,” the ‑ed is pronounced as its own syllable, “id.” For example, the ‑ed at the end of decided, hosted, and pretended are all pronounced “id.”
Simple past vs. simple present perfect
The simple past isn’t the only way to talk about events in the past in English—there’s also the simple present perfect.
So how do you know when to use one form or the other?
Meanwhile, the simple present perfect (have/has + past participle) is used for events that started in the past but have some connection to the present (perhaps they’re still continuing today, might happen again, or are affecting something in the present).
Depending on which one you use, the meaning of your sentence will change:
| Simple past | Simple present perfect | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | I watched the show every day for ten years. | I’ve watched the show every day for ten years. |
| Implies | The action started in the past and is finished. | The action started in the past and continues now. |
| Meaning | You don’t watch the show anymore. | You still watch the show. |
| Simple past | Simple present perfect | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | They ate at the restaurant three times. | They’ve eaten at the restaurant three times. |
| Implies | The action happened in the past and may not happen again in the future. | The action happened in the past and may happen again in the future. |
| Meaning | Perhaps the restaurant closed, so they know they won’t return. | They might eat at the restaurant again. |
| Simple past | Simple present perfect | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | I spilled coffee on my shirt, so I changed my clothes! | I’ve spilled coffee on my shirt, so I need to change my clothes! |
| Implies | The action happened in the past and is now complete. | The action happened in the past and is affecting the present. |
| Meaning | The spilling of the coffee caused you to have to do something in the past. | The spilling of the coffee is still affecting what you have to do now. |
Keywords to look for
There are certain words that often appear with the simple past and others that more commonly appear with the simple present perfect. These signal words are great clues to help you know which tense works best with your sentence.
Simple past signal words
- yesterday
- last ___:
- last night
- last week
- last month
- last year
- ___ ago:
- two days ago
- two weeks ago
- two months ago
- two years ago
Simple present perfect signal words
- already
- ever
- never
- once
- so far
- just
- yet
- up to now
- recently
Irregular verbs: past and past participle forms
In general, learning the past and past participle forms of irregular verbs will help you be a confident English speaker! Use the following table to help you:
| BASE VERB | PAST | PAST PARTICIPLE |
|---|---|---|
| be | was/were | been |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| break | broke | broken |
| bring | brought | brought |
| build | built | built |
| buy | bought | bought |
| catch | caught | caught |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| come | came | come |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| drive | drove | driven |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feel | felt | felt |
| find | found | found |
| fly | flew | flown |
| get | got | got or gotten |
| go | went | gone |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| lend | lent | lent |
| lie | lay | lain |
| lose | lost | lost |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| rise | rose | risen |
| run | ran | run |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| shake | shook | shaken |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sink | sank or sunk | sunk |
| sit | sat | sat |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| swim | swam | swum |
| take | took | taken |
| tell | told | told |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| understand | understood | understood |
| wear | wore | worn |
| win | won | won |
| write | wrote | written |
Make the simple past simple to learn!
Maybe in the past 😉 you were confused about the simple past, but with practice and this handy guide, you will be a simple past star! ⭐
